7 Types of Shift Work: Benefits, Challenges & How to Choose the Best Fit for Your Business
Businesses must carefully consider the types of shift schedules they offer to optimize productivity, employee satisfaction, and customer service.
In this article, we look at seven common types of work shifts, including the pros and cons of each one. Use these insights to make informed decisions and create the right shift schedule that meets your business goals and the needs of your workforce.
Use Agendrix’s workforce management software to better manage employee schedules, track clock-in/clock-out hours, manage HR, and communicate with your team
Employee Classification Types
Full-Time Employees
Full-time employees typically work fixed shifts and a standard number of hours per week (often about 40 hours a week). They are entitled to benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, and other employment perks offered by the organization.They may be paid a salary or hourly rate, depending on the company’s policies.
- Example of a full-time employee working a fixed shift: Software Engineer
Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees work fewer hours than full-time employees. The specific number of hours may vary depending on the employer and local labor laws. Part-time employees are often paid an hourly wage and may or may not receive benefits, depending on the company’s policies.
- Example of a part-time employee: Retail Sales Associate
Seasonal Employees
Seasonal employees are hired to help the company handle customer demand during its busiest time of the year. These employees usually have a firm set start and stop date of employment.
- Example of a seasonal employee: Visitor guide working at a seasonal tourism site
Temporary Employees
Temporary employees are often hired to help the company meet the needs of a particular project or to cover for a team member out on maternity or medical leave. Temporary employees usually have a set start and stop date of employment.
- Example of a temporary employee: Holiday Retail Associate
On-Call Employees
Businesses with unpredictable customer demand may prefer to hire employees who work on-call shifts. They are required to be available and ready to work on short notice if and when needed. On-call shift work may require the employee to work the first shift/morning shifts, second shift/afternoon shifts, or the third shift/evening shifts.
- Example of on-call shift work: Delivery Driver
Types of Work Shifts
1. Day Shift
The day shift refers to a work schedule that primarily occurs during the traditional daylight hours. It is the most common shift pattern and typically follows a fixed schedule aligned with the normal business hours of an organization.
- Advantages: Allows for a fixed work schedule, aligns with typical business hours, promotes work-life balance, and provides exposure to daylight.
- Disadvantages: Limited availability for certain services outside regular business hours.
- Industries most commonly used: Retail, healthcare, office settings.
- Example of this shift: Working from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM in an office setting.
2. Night Shift
The night shift, also known as the third shift or the graveyard shift, refers to a fixed shift work schedule that primarily occurs during the late evening and overnight hours. Employees who work night shifts work the same schedule each night.
- Advantages: Often pays higher wages (shift differential), less traffic and congestion during commute, potential for quieter work environment.
- Disadvantages: Disrupts natural sleep patterns, increased risk of health issues, limited social and family interactions.
- Industries most commonly used: Healthcare, manufacturing, hospitality.
- Example of this shift: Working from 11:00 PM to 7:00 AM as a night nurse in a hospital.
3. Evening Shift
The evening shift, also known as the second shift or the swing shift, refers to a work schedule that typically starts in the afternoon or early evening and extends into the night.
- Advantages: Allows for flexibility during the day, potential for differential shift pay, avoids peak-hour commuting.
- Disadvantages: Reduced time for personal commitments, limited availability for daytime activities.
- Industries most commonly used: Hospitality, customer service, call centers.
- Example of this shift: Working from 3:00 PM to 11:00 PM as customer service representatives at a call center.
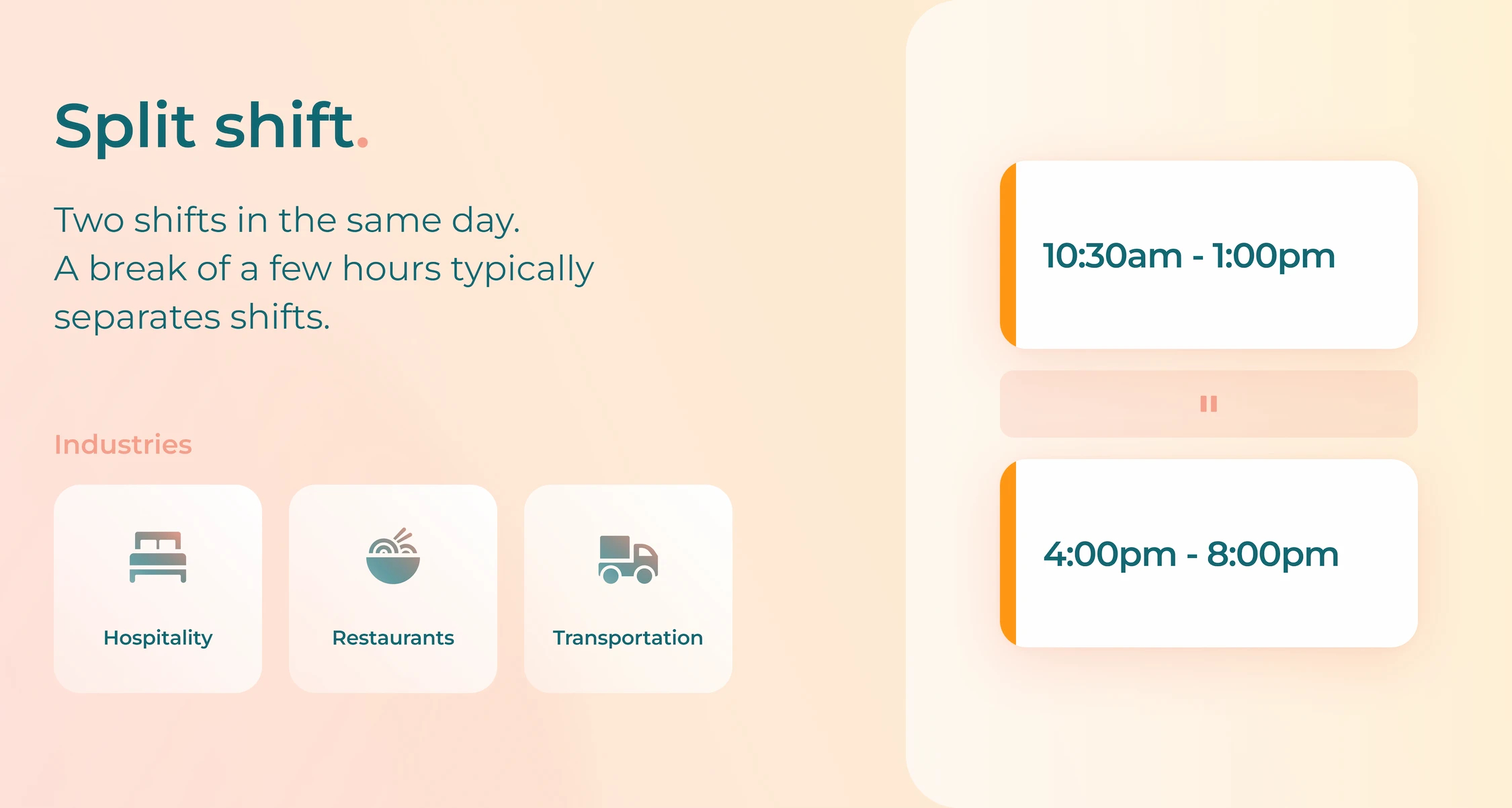
4. Split Shift
With a split shift, employees work two shifts in the same day. They work a few hours, have a fairly long break, and then return to work a few more hours later that same day.
- Advantages: A split shift work schedule provides longer breaks during the day, allows for personal appointments or activities, suits industries with fluctuating demand.
- Disadvantages: A split shift gives less contiguous free time, potential for increased commuting time and costs.
- Industries most commonly used: A split shift is most commonly used in transportation, restaurants, hospitality, childcare.
- Example of this shift: Working from 6:00 AM to 10:00 AM and then from 3:00 PM to 7:00 PM as a bus driver for the local school board or municipality.
5. Rotating Shift
A rotating shift is a work schedule that involves employees working different shifts on a rotating basis, typically including day shifts, evening shifts, and night shifts.
- Advantages: Fair distribution of shifts among employees, exposure to different work conditions and colleagues, potential for shift differentials.
- Disadvantages: Disrupts sleep patterns and personal routines, can be physically and mentally challenging.
- Industries most commonly used: Manufacturing, emergency services, transportation, healthcare.
- Example of this shift: Alternating between the morning shift (7:00 AM to 3:00 PM), the afternoon shift (3:00 PM to 11:00 PM), and the night shift (11:00 PM to 7:00 AM) on a weekly basis in a factory.
6. Weekend Shift
The weekend shift refers to a work schedule that primarily takes place on Saturdays and Sundays, typically outside of the regular weekday working hours.
- Advantages: Provides weekdays off for personal activities (schooling, another job, family obligations), potential for weekend shift differentials, less traffic during commute.
- Disadvantages: Limited availability for social events and family gatherings on weekends.
- Industries most commonly used: Retail, hospitality, healthcare.
- Example of this shift: Working on Saturdays and Sundays from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM as a caregiver in a senior’s residence.
7. On-Call Shift
An on-call shift, also known as an on-call duty or standby shift, refers to a work arrangement where employees only work if needed.
- Advantages: Flexibility in scheduling, potential for additional compensation, suits industries with unpredictable demands.
- Disadvantages: Uncertain work hours, limited ability to plan personal activities, increased stress levels.
- Industries most commonly used: Healthcare, information technology, emergency services, catering and events.
- Example of this shift: Bartender working for a catering company that does private events.
It’s worth noting that scheduling software like Agendrix offers the option to create specialized shifts, such as training shifts. These shifts allow managers to effectively track their team’s professional development and attach documents for employees to review during their training.
Create employee work schedules and instantly share them with your team. Manage time off and other requests in a single, convenient platform. Fill vacant shifts promptly for seamless operations.
How to Choose the Right Type of Work Shifts for Your Business
Below are some workforce scheduling tips to help you identify the types of work shift schedules that may be best suited for your business.
1. Assess Business Needs
Understand the specific requirements of the business, including its industry, operating hours, customer demand patterns, and workload fluctuations.
Questions to ask:
- What are the business’s goals and objectives?
- What are the constraints, such as labor costs?
- What are the legal and regulatory requirements related to scheduling?
- Are there any upsides/downsides to hiring only part time employees?
2. Evaluate Employee Preferences and Availability
Gather information about employee preferences regarding work schedule, shift hours, and flexibility. Keeping good employee records is important.
Questions to ask:
- What is the availability of each employee?
- How many hours can each employee work per day and per week?
- What constraints or limitations do employees have, such as part-time availability, childcare responsibilities, or transportation issues?
3. Consider Customer Needs
Align the work schedule with customer demands to ensure adequate staffing during busy periods.
Questions to ask:
- What is the busiest shift I need to worry about?
- What are the peak hours and days when customers require the most attention or service?
- Will seasonal workers be needed?
- How will we meet customer demand if one or more employees are absent for extended periods of time?
4. Explore Different Scheduling Options
Familiarize yourself with various scheduling options and models, such as fixed schedules, rotating shifts, split shift schedules, compressed workweeks, or flexible schedules.
Questions to ask:
- What industry best practices should we be following?
- How does each scheduling option align with the business’s needs and employee preferences?
- How will I track employee time & attendance?
If you’d like to learn more about creating a 24-hour shift schedule for your business, check out our guide: How to Create a 24-Hour Shift Schedule for Your Business + Tips.
5. Balance Workload and Employee Well-Being
Strive for a balanced workload that avoids excessive overtime or burnout while ensuring appropriate coverage.
Questions to ask:
- What are the best shift lengths, break intervals, consecutive workdays, and rest days to support employee well-being and productivity?
- How many hours should employees get off between consecutive shifts?
- Will scheduling the same employees to work the same hours improve team productivity and morale?
6. Seek Employee Input and Feedback
Involve employees in the decision-making process by seeking their input and considering their feedback. Conduct employee surveys or hold group or one-on-one discussions.
Questions to ask:
- Are you happy with your shift schedule?
- What are your preferences, concerns, and suggestions regarding shift hours and work schedules?
- Do you enjoy always working with the same employees or would you like the opportunity to occasionally work with other employees?
7. Account for Fairness and Equity
Ensure that the scheduling process is fair and equitable, avoiding favoritism or discriminatory practices.
Questions to ask:
- What factors do we need to account for when assigning shifts or considering time-off requests? (for example, seniority, skill levels, and performance)
- Are we treating our part time workers and seasonal workers fairly?
8. Test and Evaluate
Implement a proposed work schedule on a trial basis to assess its effectiveness. Seek feedback from employees and make necessary adjustments based on the evaluation results.
Questions to ask:
- What impact is the trial schedule having on employee morale, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance?
- How is the shift schedule affecting sleep schedules?
9. Review and Adapt
Regularly review the chosen work schedule to ensure it continues to meet the evolving needs of the business and its employees.
Questions to ask:
- What industry trends and external/internal changes may require adjustments to the work schedule over time?
- Are employees working too many overtime hours? Do we need to start recruiting more part-time workers?
By considering these factors and asking relevant questions, managers and business owners can make informed decisions when choosing the right type of work schedule that maximizes employee satisfaction, productivity, and operational efficiency.
How to Go About Shift Scheduling
The follow scheduling strategies will help you ensure your work schedule meets both business and employee needs:
1. Identify Staffing Needs
Determine the number of employees required for each shift based on factors such as anticipated workload, customer demand, and employee availability.
2. Collect Employee Availability
Request employees to provide their availability for different shifts, taking into account their preferences, time-off requests, and any constraints they may have.
3. Consider Business Requirements
Align employee availability with the needs of the business, ensuring that there is adequate coverage during peak hours and busy periods.
4. Create a Schedule Template
Use or create a schedule template that includes regular shift patterns, such as morning, afternoon, and evening shifts, and assign specific roles or responsibilities to each shift.
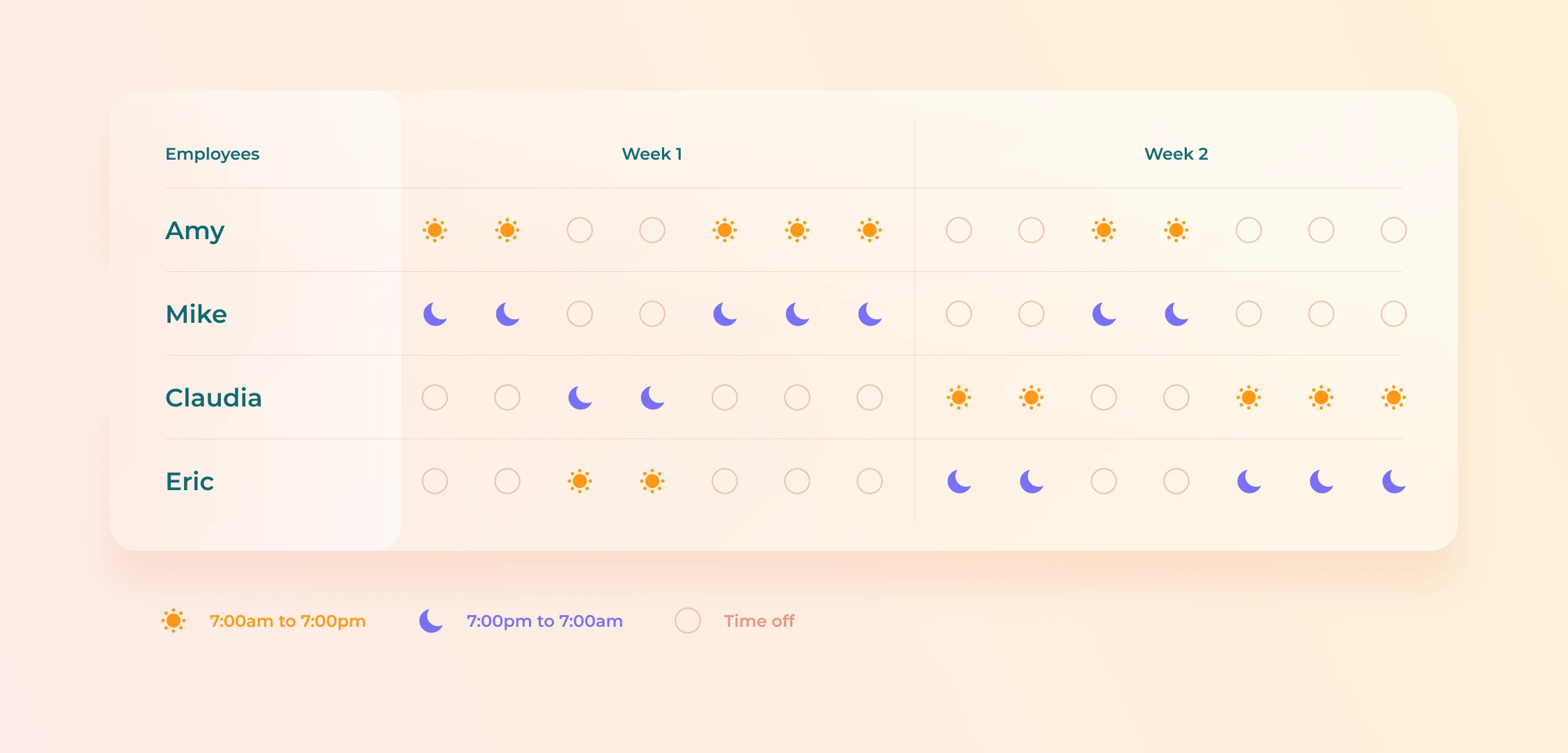
Example of how to set up a 2-2 / 3-2 / 2-3 (2 on, 2 off; 3 on, 2 off; etc.) shift schedule for a team of 4 employees working at manufacturing plant:
All 4 employees rotate through the same cycle of day shifts, night shifts, and days off. They all start at different times to ensure full coverage during business hours.
5. Assign Shifts
Assign employees to specific shifts based on their availability, skills, seniority, and any specific requirements of the role or task. There are different employee scheduling software options available that make it easy to take various constraints into account when scheduling employees.
6. Review and Adjust
Review the initial schedule for any conflicts or gaps in coverage and make adjustments as necessary. This may involve resolving scheduling conflicts, accommodating time-off requests, and balancing workload across shifts.
7. Communicate the Schedule
Once the schedule is finalized, communicate it to employees in a clear and timely manner. Provide them with access to their schedule and ensure they understand any special instructions or changes.
8. Monitor and Manage Changes
Continuously monitor the schedule for any changes, such as employee requests for shift swaps or unexpected absences. Have a system in place to manage and track these changes effectively.
9. Seek Feedback and Improvements
Regularly gather feedback from employees regarding the schedule to identify areas for improvement. Consider their preferences, concerns, and suggestions when making future scheduling decisions.
By following these steps, employers can effectively schedule work shifts for their employees, ensuring appropriate coverage, employee satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to effective employee management. With careful planning and thoughtful consideration, you can create a work schedule that enhances productivity, fosters employee well-being, and propels your business towards success.
Determine your business needs, find out what your employees prefer, and use scheduling software to easily create and manage your shift work schedules.
Not ready to try scheduling software just yet? Explore our free employee work schedule templates.
What Are the Most Common Work Shifts?
- Day shift: This shift typically spans the traditional working hours of the day, usually from morning to early evening. It is commonly found in industries such as healthcare, administrative roles, customer service, and office-based jobs.
- Evening shift: Also known as the second shift or the swing shift, this shift usually starts in the afternoon or early evening and extends into the night. It is commonly seen in industries like hotels & hospitality, retail, manufacturing, and transportation.
- Night shift: Night shifts typically run during the late evening and overnight hours, providing coverage during non-traditional working times. It is common in industries such as healthcare (for nurses and medical staff), emergency services, security, and certain manufacturing operations.
- Rotating shifts: Rotating shifts involve the same employees working different shifts on a rotating basis, which can include day, evening, and night shifts. This type of shift system ensures around-the-clock coverage and may be found in industries like manufacturing, emergency services, and continuous operations.
- Split shifts: Split shifts involve dividing the workday into multiple shifts, where employees have an extended break or time off in between. This shift pattern is commonly used in industries such as transportation, hospitality, and healthcare.
- Weekends and holidays: Some industries, such as retail, hospitality, and healthcare, require employees to work on weekends and public holidays to meet customer demands and ensure continuity of service.
What Is the Healthiest Work Shift?
The healthiest work shift for a given employee can depend on various factors such as:
- Individual preference
- Lifestyle
- Circadian rhythm
However, research suggests that maintaining a consistent and regular work schedule, particularly during daytime hours, can be beneficial for overall health and well-being. Here are a few considerations:
- Day shift: Daytime work shifts that align with the natural sleep-wake cycle and allow for sufficient restorative sleep at night are generally considered healthier. Day shifts are associated with better sleep quality, reduced risk of sleep disorders, and improved mental and physical health outcomes.
- Regular schedule: Having a consistent and predictable work schedule, such as fixed shifts or a regular rotation, can promote stability and allow for better planning of personal activities, sleep routines, and social interactions. Regular schedules also support circadian rhythm synchronization, which is important for optimal health.
- Adequate rest and recovery: Ensuring adequate time off between shifts, including rest days and breaks, is crucial for recovery and avoiding fatigue. Long work hours, excessive overtime, or inadequate rest periods (such as scheduling employees for the “clopening” shift) can lead to increased stress, sleep deprivation, and higher risks of accidents or health issues.
- Flexibility and autonomy: Providing employees with some flexibility and control over their schedules can contribute to better work-life balance and overall well-being. Options such as flexible shift work hours, compressed workweeks, or the ability to swap shifts can help employees manage personal commitments and reduce work-related stress.
Bear in mind that individual responses to different types of work shifts can vary. Some shift workers may prefer or adapt better to non-traditional or non-daytime shift work. Managers should consider employee preferences and engage in open communication with shift workers to create a supportive work environment that promotes both physical and mental health.